|
| |
Process Improvement:
We specialize in energy systems, power cycle chemistry and
water treatment, for any industry. Although utility systems may not be a
profit centre, paying attention to your utility systems can yield attractive
returns. The US Department of Energy has stated that an energy audit and improvement program for a typical industrial
facility can save 20% in steam related costs. In the USA alone, this would
save
US$4 Billion dollars per year and avoid approximately 32 million tonnes of emissions
reduction. Typical savings that we can help
your organization achieve include:
- 10-12% improvement by improving water treatment program
to prevent formation of insulating boiler scale.
- Minimizing stack gas energy losses (improve boiler
efficiency by 1% for each 15% reduction in excess air or 1.3% reduction in
oxygen, or, for each 40 degrees F stack gas temperature reduction).
- Improve recovery of condensate and it's heat content.
- 10-15% energy savings can be realized when steam traps
are actively maintained.
- 2-5% with boiler and auxiliary equipment tune-ups.
- 3-13% savings may be realized with improved insulation.
- Cooling water system audit and tune-up may improve heat
transfer rates and heat exchanger water side cleanliness to increase plant
production rates, extend equipment life, and virtually eliminate downtime
for heat exchanger cleaning.
Quantification of the savings opportunity is a key first
step towards achieving your plant's full potential. Often this is not
done as water and energy costs appear small on a company's balance sheet, and
many may see it as an uncontrollable cost of doing business.
Utility operation reliability is of much higher importance. Implementation of efficiency improvements typically also enhance the system's
reliability. We will help you to reduce costs and improve reliability to
help achieve your
plant's full potential.
 For
new assets, utility system detailed design work typically begins last,
yet construction must be completed first. Design activity is concentrated within a short time
frame, requiring increased staff hours for a short period. This is a key
time, as up to 80% of a
project's capital expenditure is typically determined at this stage. Significant savings can
be realized, by applying specialized experience early in the project
phases. At this in the design, DeltaCascade's service provides the highest
value. For
new assets, utility system detailed design work typically begins last,
yet construction must be completed first. Design activity is concentrated within a short time
frame, requiring increased staff hours for a short period. This is a key
time, as up to 80% of a
project's capital expenditure is typically determined at this stage. Significant savings can
be realized, by applying specialized experience early in the project
phases. At this in the design, DeltaCascade's service provides the highest
value.
Water
systems are essential to industrial
installations, whether it be influent water, boiler
water, steam or condensate, cooling water, process water, or wastewater
systems. Used as a heating or a cooling agent or as a feed stock, effective design and operation of water
 systems is likely
critical to your operations. systems is likely
critical to your operations. Yet, in most
industries, as water related systems are typically not
identified as profit centres, water related
opportunities for improvement are often overlooked. DeltaCascade can help
you identify and quantify undiscovered opportunity for improvement, often of significant proportion. Process
Improvement Services (Operating
Facilities)
| Water System Audits for
Process
Improvement Opportunity Identification
|
Influent Water Systems |
| Boiler Water, Steam and Condensate Systems |
| Cooling Water Systems |
| Wastewater Systems |
| Energy System Audits for Process
Improvement
|
Steam system audit to optimise energy use and
water use (eg: minimize
venting) |
| Scale and corrosion protection
enhancement |
| Integration Opportunities
|
Site
energy and water system mass balance
modelling, needs
assessment, improvement opportunity identification and implementation |
| Plant Start-up
and Shutdown/Turnaround Assistance |
Chemical cleaning and passivation coordination |
| Commissioning |
| Equipment Lay-up |
| Training
|
Operator Process Training |
| Statistical Process Control
and Quality Improvement |
| Procedures and Manuals Development |
| Process Design,
Procurement and Construction
|
Implementation
of Identified Improvement Opportunities |
Typical Benefits
| Increased Revenue |
Increase plant production rates |
| Extend run time between shutdowns |
| Improve plant reliability |
| Improve process input quality |
|
Reduced Costs
|
Reduce chemical and mechanical inputs |
| Reduce process waste |
| Improved Environmental
Performance
|
Reduce effective greenhouse gas emissions |
| Improve plant effluent water quality |
| Reduce plant effluent water quantity |
| Reduce plant water demand |
 Sample
Water System Opportunities: Sample
Water System Opportunities:
Influent
Water Systems Influent water quality and treatment is key to
effective, optimal operation of all downstream equipment. Problems and
opportunities encountered might include:
- Supply Water: If supply water quality varies, such as with river water
intakes during seasonal run-offs or storms, seasonal adjustments to process
operations may be required. This maybe as simple as drawing from
holding ponds instead of river during peak spring-run off periods, or
changing a cold lime softener to clarification only mode by interruption of
lime feed. Backwash rates of filters and other packed beds such as ion
exchange vessels, must be reduced in winter and increased in summer to
account for temperature and viscosity changes. A system audit may
uncover some simple improvements that may have been overlooked.

- Clarification: If you clarify influent water, and have poor
or variable performance, a clarifier audit may be of value. Audits
will review operating practice identifying improvements, in areas such
as: water flow control, temperature control, chemical feed control, sludge level
control and chemical treatment regime.
Pilot tests or jar test
studies can also be performed.
- Lime Softening: Performance improvement of these units
greatly improve performance of downstream systems, such as demineralisers
for boiler make-up water supply. Lime slurry feed
problems may present improvement opportunity. One plant added heat
exchange to raise softening temperature, which improves softening
ability. However, temperature control was overlooked, resulting in
temperature inversions in the softener, and severe intermittent sludge carry-over
problems. Installing temperature control reduced average temperature
increase, but alleviated the upset problem and improved overall performance.
As for clarification, an audit may enable significant improvement in asset performance.
- Demineralisation: Demineralisation plants are a work horse of
industry. As they operate in a semi-batch mode, they can be challenging to
troubleshoot. Performance degradation must be monitored, managed and
minimised. Ion exchange resins must be kept clean, and, particularly for
 anion resins,
typically must be intermittently cleaned to
minimise irreversible fouling. Demin plant audits can identify needs
and improvement opportunities, such as reducing wastewater production and
reducing caustic and acid regenerant coonsumption. Training courses can similarly assist. anion resins,
typically must be intermittently cleaned to
minimise irreversible fouling. Demin plant audits can identify needs
and improvement opportunities, such as reducing wastewater production and
reducing caustic and acid regenerant coonsumption. Training courses can similarly assist.
One demin plant installation committed a simple act of discharging alkaline anion-regeneration waste to their
neutralization sump prior to discharge of acidic
cation-regeneration waste. The result was a milky precipitation of alkaline
salts which did not settle but did collect nearer to the bottom of the vessel.
This caused difficulty with waste water pH control, with additional caustic
feed for neutralization. Downstream effluent ponds experienced mysterious pH
rises during recirculation prior to discharge, due to slow re-dissolved of
alkaline precipitates. In addition to control problems, this led
to costly dredging operations at effluent water ponds to be required.. A simple fix in the demin plant operation procedures,
is to ensure that acidic waste is discharged to neutralization tank prior to alkaline
waste. This would avoid downstream pH control
difficulties due to formation of alkaline flocc.
- Reverse Osmosis or other treatment process may be required,
particularly for high pressure boilers when supply water is high in
colloidal silica or very high in dissolved solids. Water quality
control at and upstream of the RO system is key to optimal RO process
operation, otherwise, membrane life may be reduced, and RO operation costs
skyrocket. Minimization of RO reject stream is also important to
reduce wastewater production and related costs, balancing against shortened
membrane life.
Boiler Water Systems
Steam
cycle chemistry plays an important role in efficiency and reliability of boiler
systems, as well as steam and condensate systems. If boiler tube failures are
interrupting your production or extending your planned shutdown periods, you may benefit from a boiler water system
audit. Your problem may be as simple as oxygen saturated water
contamination of condensate causing corrosion, and subsequent deposition of iron
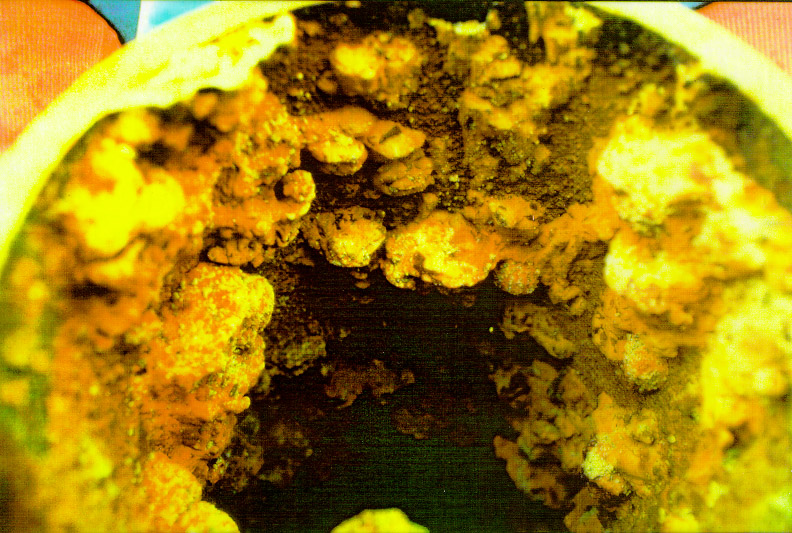
deposits on boiler tubes.  The insulating iron deposits lead to tube overheat and
failure. The insulating iron deposits lead to tube overheat and
failure.
One facility was found to be using a low pressure boiler water treatment
product for a higher pressure boiler with a steam super-heater and steam
turbine which required high purity steam. Super-heater tube failure frequency
was increasing. The treatment product contained phosphate treatment
chemical in potassium, rather than the anticipated sodium, form. Steam
purity studies using standard sodium electrode procedure indicated acceptable steam
purity. Analysing for potassium, and then modifying the boiler water
treatment program to use sodium based phosphate treatment, enabled a corrosive steam solids
contamination to be identified and controlled through improved boiler water level control.
Cooling Water Systems
Evaporative cooling towers, while efficient heat sinks, and effective water
conservers compared to once through cooling, may be the largest
water consumer and wastewater generator at your site. While
cooling systems are often designed to operate at about 8 cycles of  concentration
(12.5% blow-down), they can very often effectively operate at 12 cycles (8%
blow-down) or higher. This reduces raw water demand by over 4% and reduces wastewater
production rate by approximately one third. It may also reduce chemical
treatment program costs. In
addition, cooling water systems present excellent opportunity for integration of
processes to enable water recycle and re-use. Treated sanitary waste
water, a controlled amount of boiler blow down water, some demin plant waste waters, and other streams,
may be used as cooling system make-up water, reducing raw water demand and wastewater production. concentration
(12.5% blow-down), they can very often effectively operate at 12 cycles (8%
blow-down) or higher. This reduces raw water demand by over 4% and reduces wastewater
production rate by approximately one third. It may also reduce chemical
treatment program costs. In
addition, cooling water systems present excellent opportunity for integration of
processes to enable water recycle and re-use. Treated sanitary waste
water, a controlled amount of boiler blow down water, some demin plant waste waters, and other streams,
may be used as cooling system make-up water, reducing raw water demand and wastewater production.
Cooling water flow mal-distribution is a common problem at industrial
facilities. Numerous heat exchangers and piping networks typically
exist between cooling water supply and return headers. Hence, flow
restrictions at certain exchangers cannot typically be determined by monitoring
pressure drop. Flow restrictions may be
difficult to identify unless equipment has a high level of instrumentation. Equipment near the end of
cooling water headers are particularly prone to becoming clogged with debris, as
the debris has more difficulty taking corners, than following to the end of the
pipe. Cooling towers are essentially big air washers, so that small bore tube exchangers may become clogged following
wind storms, and remain clogged with seeds, fluff, dirt and debris, with elevated fouling and corrosion rates, until
serviced. Resulting cooling water flow reduction reduces heat exchange rates.
More seriously, the accompanying low water velocity insidiously contributes to
heat exchange surface fouling and under-deposit corrosion. Corrosion
products contaminate the entire system, compromising both corrosion control and
scale control performance throughout the entire plant. A cooling water flow survey with portable ultrasonic flow
meter can be helpful to identify problem areas for correction.
Hydraulic analysis of the entire cooling water system piping network,
particularly prior to system piping modifications or expansions, can help avoid problems of system
fouling, under-deposit corrosion and heat transfer related production
bottlenecks. When designing side-stream filters, it may be prudent to have
the filter feed water take-off from the re-circulating cooling water at the
outside of any available pipe bends, to enhance capture of debris by the filters
for the life of the plant.
Wastewater Systems
Minimization of waste water production is a primary opportunity for improving
wastewater systems performance. Optimising influent water treatment systems,  and
taking advantage of water re-use and recycle and other process integration
opportunities, can pay significant benefit. and
taking advantage of water re-use and recycle and other process integration
opportunities, can pay significant benefit.
In addition to waste water process audit in itself, quality control of water
feeding the waste treatment process presents another significant
opportunity. Eliminating slugs of impurities through process integration
and, or, quality control programs can be highly effective.
Contact us if we can help with your water system questions, or participate with
you in problem solving and process improvement work.
|